-
Newsfeed
- ERKUNDEN
-
Seiten
-
Veranstaltungen
-
Blogs
Fuel Cell for Data Center Market Revenue Boosted by Off-Grid Power Solutions
Introduction: Transforming Data Center Power Solutions
The exponential growth of cloud computing, artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and edge computing has significantly increased the demand for reliable and sustainable power solutions in data centers. As digital infrastructure expands globally, operators are seeking cleaner and more efficient alternatives to traditional diesel generators and grid-based electricity. Fuel cells have emerged as a promising technology, offering low emissions, high efficiency, and dependable backup or primary power capabilities. The fuel cell for data center market is gaining momentum as enterprises prioritize energy resilience, carbon reduction, and long-term operational stability.
Market Overview and Growth Outlook
The fuel cell for data center market is experiencing rapid expansion, driven by the urgent need for sustainable and uninterrupted power supply systems. Data centers require consistent, high-quality power to prevent downtime, which can lead to significant financial and reputational losses. Fuel cells provide a decentralized energy solution capable of delivering continuous electricity with minimal environmental impact.
According to Persistence Market Research, the global fuel cell for data center market is expected to witness remarkable growth over the forecast period. The market size is anticipated to reach approximately US$ 361.1 million in 2026 and is projected to surge to US$ 1,192.0 million by 2033. This impressive expansion represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.6% between 2026 and 2033. The strong growth trajectory reflects increasing investments in green data centers, rising regulatory pressures to reduce emissions, and advancements in fuel cell technology.
Why Are Fuel Cells Gaining Popularity in Data Centers?
Fuel cells are becoming increasingly popular in data centers due to their ability to provide reliable, low-emission, and scalable power solutions. Unlike traditional backup generators that rely on diesel and contribute to carbon emissions, fuel cells generate electricity through an electrochemical process, typically using hydrogen or natural gas. This process produces significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions and can operate continuously without the mechanical wear and tear associated with combustion engines.
Another key factor driving adoption is resilience. Fuel cells can operate independently of the grid, making them ideal for ensuring uninterrupted power during outages. In regions prone to natural disasters or grid instability, data center operators are turning to fuel cells to enhance reliability and reduce operational risks. Additionally, the modular design of many fuel cell systems allows operators to scale capacity as demand grows, making them suitable for hyperscale and edge data centers alike.
Get Your FREE Sample Report Instantly – Click Now
How Do Fuel Cells Improve Data Center Energy Efficiency and Sustainability?
Fuel cells improve data center energy efficiency and sustainability by converting chemical energy directly into electricity through an electrochemical reaction, eliminating combustion and reducing energy loss. This results in higher efficiency levels compared to conventional diesel generators and grid-based power systems. Fuel cells can achieve efficiencies of up to 60% or higher, and when combined with combined heat and power (CHP) systems, overall efficiency can exceed 80%. Additionally, fuel cells produce significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions, especially when powered by green hydrogen or biogas. Their ability to operate continuously with minimal noise and pollutants makes them an ideal solution for sustainable data center operations focused on carbon neutrality and long-term environmental goals.
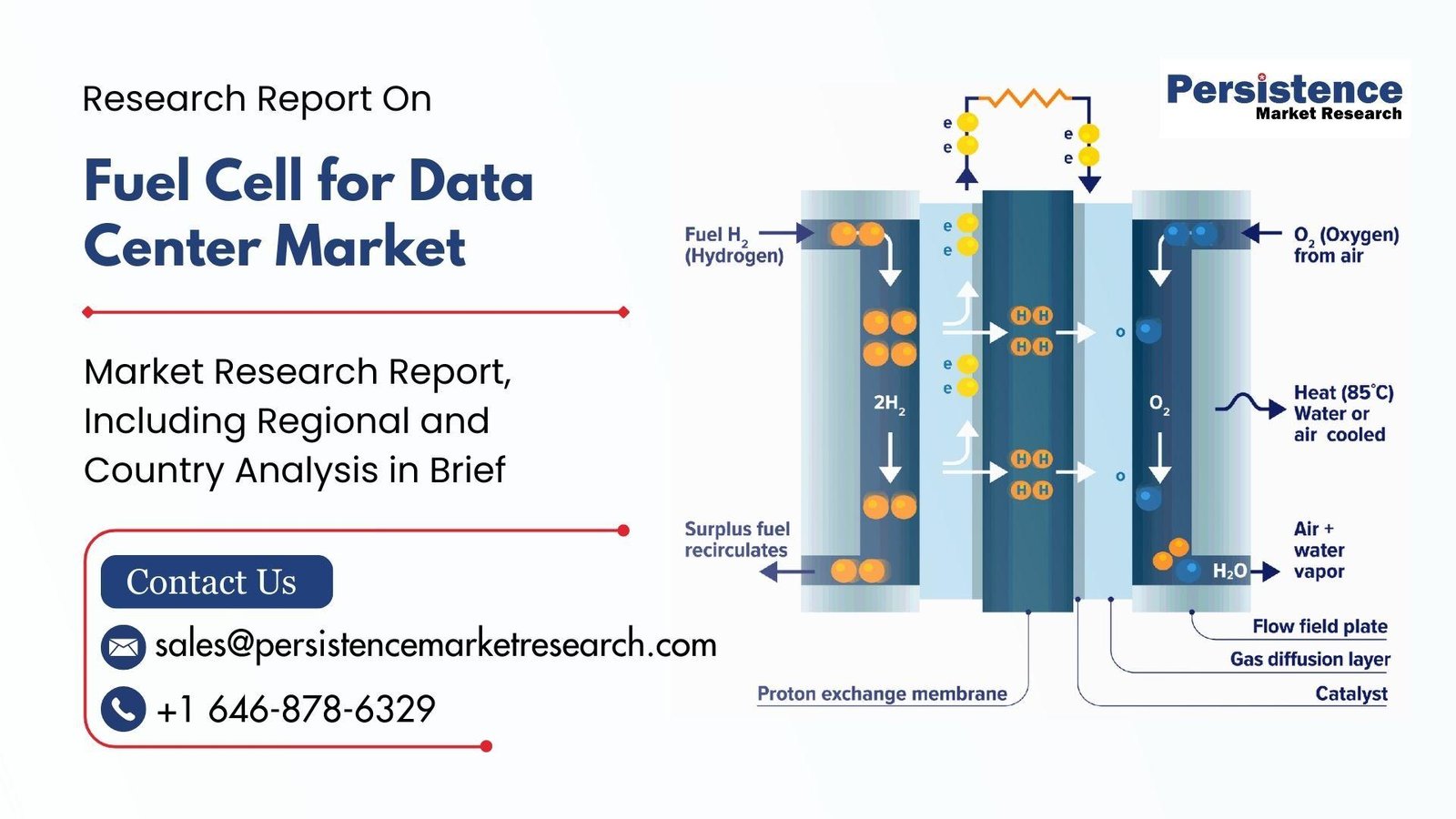
Technology Landscape: Types of Fuel Cells in Data Centers
Several types of fuel cells are being deployed in data center environments, with the most common being solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC) and proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells. Solid oxide fuel cells operate at high temperatures and are often fueled by natural gas or biogas. They are well-suited for continuous base-load power generation and are widely adopted in large-scale data centers due to their durability and efficiency.
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells, on the other hand, operate at lower temperatures and typically use hydrogen as fuel. PEM fuel cells are known for their quick startup times and responsiveness, making them suitable for backup power applications. As the hydrogen economy evolves and green hydrogen production scales up, PEM fuel cells are expected to play a larger role in the data center power ecosystem.
Drivers Accelerating Market Growth
One of the primary drivers of the fuel cell for data center market is the increasing emphasis on sustainability and decarbonization. Major technology companies have committed to achieving net-zero carbon emissions, prompting them to explore cleaner energy alternatives. Fuel cells align well with these sustainability objectives by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing carbon footprints.
Rising electricity costs and grid reliability concerns are also contributing to market growth. In many regions, aging infrastructure and peak demand pressures are leading to frequent outages and voltage fluctuations. Fuel cells offer a stable and predictable power source, helping operators mitigate these risks. Furthermore, government incentives, tax credits, and funding programs aimed at promoting clean energy technologies are encouraging investment in fuel cell installations for data centers.
Regional Insights and Adoption Trends
North America currently leads the fuel cell for data center market, driven by strong technology infrastructure, supportive government policies, and the presence of leading fuel cell manufacturers. The United States, in particular, has witnessed significant deployment of fuel cell systems in data centers operated by major cloud service providers and colocation facilities.
Europe is also experiencing steady growth, supported by stringent emission regulations and ambitious climate targets. Countries such as Germany and the United Kingdom are investing in hydrogen infrastructure and renewable energy integration, creating favorable conditions for fuel cell adoption.
Asia-Pacific represents a high-growth region, fueled by rapid digitalization, expanding data center capacity, and government initiatives promoting hydrogen energy. Countries like Japan and South Korea are at the forefront of hydrogen technology development, which could further accelerate fuel cell deployment in data centers across the region.
Challenges and Market Constraints
Despite the strong growth outlook, the fuel cell for data center market faces certain challenges. High initial capital costs remain a significant barrier, particularly for small and medium-sized data center operators. Although operational costs may be lower over time, the upfront investment required for fuel cell systems can be substantial.
Fuel availability and infrastructure limitations also pose challenges, especially for hydrogen-based systems. The development of a robust hydrogen supply chain is critical for scaling PEM fuel cell adoption. Additionally, technological complexities and maintenance requirements may require specialized expertise, increasing operational considerations for facility managers.
Integration with Renewable Energy and Microgrids
One of the most promising developments in the fuel cell for data center market is integration with renewable energy sources and microgrid systems. Fuel cells can complement solar and wind power by providing stable baseload electricity when renewable generation fluctuates. This hybrid approach enhances energy reliability and supports carbon-neutral operations.
Microgrids incorporating fuel cells allow data centers to operate independently from the main grid during emergencies. This decentralized energy model not only improves resilience but also enables better energy management and cost optimization. As smart grid technologies advance, fuel cells are expected to become an integral component of next-generation energy systems for digital infrastructure.
Future Outlook: Innovation and Strategic Opportunities
The future of the fuel cell for data center market appears highly promising, with rapid technological advancements and increasing investment in clean energy solutions. Innovations in fuel cell efficiency, cost reduction, and hydrogen production are likely to enhance the commercial viability of these systems. As economies of scale are achieved and manufacturing processes improve, prices are expected to decline, making fuel cells more accessible to a broader range of data center operators.
Strategic partnerships between fuel cell manufacturers, energy providers, and technology companies will further drive market expansion. With the market projected to grow from US$ 361.1 million in 2026 to US$ 1,192.0 million by 2033 at a CAGR of 18.6%, the industry is positioned for sustained and transformative growth.
Conclusion: Powering the Digital Future Sustainably
As the world becomes increasingly dependent on digital services, the need for reliable and sustainable power solutions in data centers is more critical than ever. Fuel cells offer a compelling alternative to conventional energy sources, combining efficiency, resilience, and environmental benefits. With strong market growth projections and expanding technological capabilities, the fuel cell for data center market is set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of sustainable digital infrastructure.
Explore the Latest Trending Research Reports:
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spiele
- Gardening
- Health
- Startseite
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Andere
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
